Nails and Pins
From DT Online
Most Nails are made from cold drawn mild steel wire. This process improves the strength or wire by work hardening such that Nails can be driven into timber by use of Hammers. If nails do become bent they can easily be withdrawn using Pincers or a Claw Hammer for example.
The holding power of nails depends upon Friction and some nails have coatings or grips designed into the body of the nail (i.e. shank) to improve this. In addition, some coatings are applied to improve resistance to corrosion (e.g. Galvanising). Nails may be driven in at opposing angles as shown. This is a process known as Dovetail Nailing and also improves their holding power.
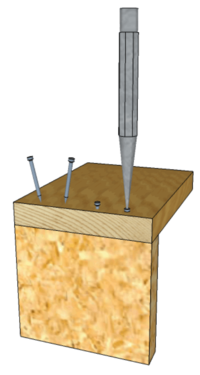
Shown opposite is the use of a Nail Punch. It is good practice on fine work to drive nails in to a few millimeters of the surface then punch them below it. The punched hole can then be filled with Wood Filler.
When using nails in softwoods they can usually be driven in directly but for hardwoods, and sometimes to avoid splitting near the end on any timbers, a small hole may be drilled in the top piece first - or bored with a Bradawl.
Safety Point! Builders may also use Nail Guns but these are extremely dangerous and not suitable for school use.
| Round Wire Nails | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |
| Oval Wire Nails | # | |
| Panel Pins | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |
| Ring Nails | # | |
| Corrugated Fasteners | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |
| Tacks | # | |
| Upholstery Tacks | # | |
| Clout Nails | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |
| Floor Brad | # | |
| Fencing Staples | # | |
| Masonry Nails | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |
| # | # | [[File:###|100px|right]] |