Neutral Axis: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m (Added images) |
m (Added links) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
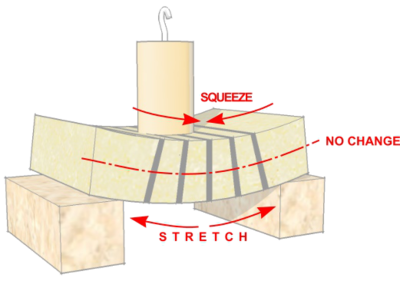
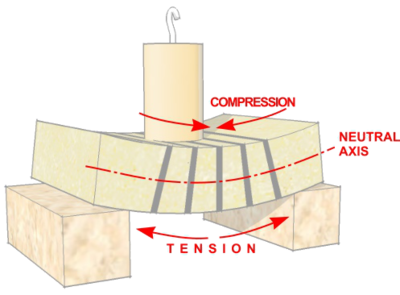
As beams bend, the top experiences forces which squeeze it together ''(compression)'', and the bottom of the beam is stretched ''(tension)''. But the centre line of the beam is unaffected and is known as the '''Neutral Axis'''. | As beams bend, the top experiences forces which squeeze it together ''('''[[Compression|compression]]''')'', and the bottom of the beam is stretched ''('''[[Tension|tension]]''')''. But the centre line of the beam is unaffected and is known as the '''Neutral Axis'''. | ||
:::[[File:SpongeNeutralAxis.png|400px|bottom]][[File:SpongeNeutralAxis2.png|400px|bottom]] | :::[[File:SpongeNeutralAxis.png|400px|bottom]][[File:SpongeNeutralAxis2.png|400px|bottom]] | ||
Simple beam bridges have to withstand all these forces which due to their own weight and the loads which are applied. If the material used is unsuitable it will break ''(e.g. like a stick of chalk)'', or if there is not enough of it to share the loads within it, then the beam may collapse ''(e.g. as | Simple beam bridges have to withstand all these forces which due to their own weight and the loads which are applied. If the material used is unsuitable it will break ''(e.g. like a stick of chalk)'', or if there is not enough of it to share the loads within it, then the beam may collapse ''(e.g. as a [[Finding out about forces in a simple beam|thin sheet of card would]])''. | ||
[[Category:Terminology]] | [[Category:Terminology]] | ||
[[Category:Beams]] | [[Category:Beams]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:57, 20 December 2015
As beams bend, the top experiences forces which squeeze it together (compression), and the bottom of the beam is stretched (tension). But the centre line of the beam is unaffected and is known as the Neutral Axis.
Simple beam bridges have to withstand all these forces which due to their own weight and the loads which are applied. If the material used is unsuitable it will break (e.g. like a stick of chalk), or if there is not enough of it to share the loads within it, then the beam may collapse (e.g. as a thin sheet of card would).