Polygons: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
(Completed text and added category links) |
(Completed Pentagon) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
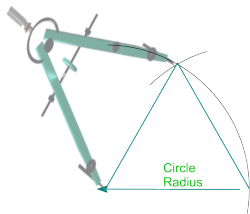
* Draw a line of length equal to the length of side required. | * Draw a line of length equal to the length of side required. | ||
* From each end of the line, strike arcs using the line length as radius. | * From each end of the line, strike arcs using the line length as radius. | ||
* Where they intersect will provide the top apex of the required triangle. </span> | * Where they intersect will provide the top [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apex_%28geometry%29 '''apex'''] of the required triangle. </span> | ||
| [[File:CompassTriangle.png|250px|right]] | | [[File:CompassTriangle.png|250px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| <span style="color:#B00000"> | | <span style="color:#B00000"> | ||
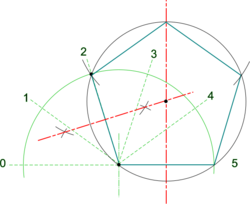
* Draw a line of length equal to the length of side required and construct its perpendicular bisector - (see '''[[Basic Constructions]]'''). | * Draw a line of length equal to the length of side required and construct its perpendicular bisector - (see '''[[Basic Constructions]]'''). | ||
* Draw a semi-circle at one end of the line and divide its circumference into as many equal parts as there are polygon sides required ''(5 in this case)'' | |||
* The line connecting the semi-circle centre to the 2nd point is a side of the required polygon ''(pentagon) in this case. | |||
* Construct the perpendicular bisector of this second side to intersect with that drawn for the base line. | |||
* Where the two bisectors intersect is the centre for a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circumscribed_circle '''circumscribing circle'''] to the required polygon. | |||
* Draw the circle and step off the required number of sides. | |||
---- | ---- | ||
<span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | <span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | ||
Polygons with odd numbered sides have an apex at top centre and this can be used for greater accuracy as an alternatve starting point, or as check, when stepping off sides round the circle . | Polygons with odd numbered sides have an apex at top centre and this can be used for greater accuracy as an alternatve starting point, or as check, when stepping off sides round the circle . | ||
</span> | |||
---- | |||
<span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | |||
This construction may be used for other polygons by stepping off an appropriate number of sides around the semi-circle - but in all cases always start by drawing a lne through the 2nd division to establish the circumscribing circle centre. | |||
</span> | </span> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 19:52, 25 February 2015
Drawing regular Polygons is now most easily accomplished using modern drafting aids and Computer Aided Design tools. But there are occasions when it is useful to have an understanding of some basic constructions using just rule and compasses (or pegs and pieces of string). Examples might include large scale work for stage sets or carnival floats, or on-site work for buildings, playgrounds, sports fields and gardens.
The following examples are limited to constructions of regular polygons. Irregular polygon construction may be achieved using a process of triangulation, vectors, coordinates or plotting points on a matrix for example. Some other polygons (e.g. Cyclic Quadlitateral) have particular properties which can be helpful to know when constructing them.
See also the YouTube video All the possible polygons!. This shows how all regular polygons can be constructed using classical geometry techniques
Note: Some constructions on the YouTube video may be different to those described below - there are several methods of construction possible for most regular polygons.
| Equilateral Triangle |
|
|
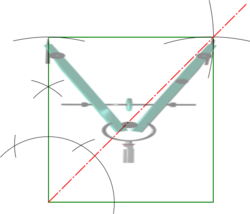
| Square |
|
|
| Pentagon |
Note: Polygons with odd numbered sides have an apex at top centre and this can be used for greater accuracy as an alternatve starting point, or as check, when stepping off sides round the circle . Note: This construction may be used for other polygons by stepping off an appropriate number of sides around the semi-circle - but in all cases always start by drawing a lne through the 2nd division to establish the circumscribing circle centre.
|
|
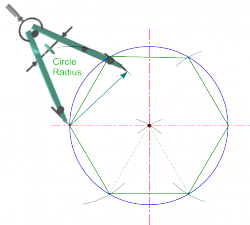
| Hexagon |
Note: Polygons with even numbers of sides have diagonals parrallel to the sides and this can be used as a check on accuracy
|
|
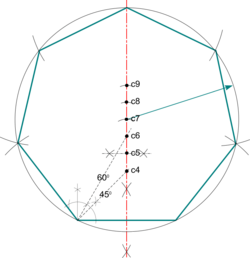
| Septagon |
Note: This circle would circumscribe a pentagon and provides an alternative construction.
|
|
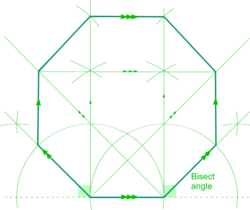
| Octagon |
|