Solenoid: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m (Added category links) |
m (Corrected category link) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Category:Primary]] | [[Category:Primary]] | ||
[[Category:Secondary]] | [[Category:Secondary]] | ||
[[Category:Electronics and Control]] | [[Category:Electronics and Control]] | ||
[[Category:Materials and Components]] | |||
Revision as of 21:34, 30 April 2015
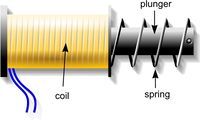
A solenoid is a coil of wire wrapped around a former. The plunger is free to move and is attracted into the coil when a current flows in the coil. When the current is turned off, a spring pushes the plunger out of the coil.
Solenoids are used for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy (transducer) in the form of linear motion.
They are current and voltage rated and attention must be taken to prevent these limits from being exceeded.
Uses include electrical door locks and model animation.