BC108 Transistor: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m (Added category links) |
m (Added image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:BC108.png|250px|right]] | |||
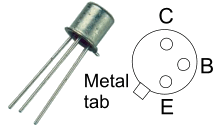
The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BC548 '''BC108'''] Collector is connected to the positive (+ve) supply via the load. NB: If the load is inductive i.e. has coil windings such as a relay, solenoid or motor, then it is usual to connect a diode across it to prevent the Back EMF from damaging the transistor. (Cathode to supply). | The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BC548 '''BC108'''] Collector is connected to the positive (+ve) supply via the load. NB: If the load is inductive i.e. has coil windings such as a relay, solenoid or motor, then it is usual to connect a diode across it to prevent the Back EMF from damaging the transistor. (Cathode to supply). | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 1 June 2015
The BC108 Collector is connected to the positive (+ve) supply via the load. NB: If the load is inductive i.e. has coil windings such as a relay, solenoid or motor, then it is usual to connect a diode across it to prevent the Back EMF from damaging the transistor. (Cathode to supply).
The input is connected to the Base via a limiting resistor (typically 1K). The Emitter is connected to the negative (-ve) supply (0V).
Uses: As current amplifiers and electronic switches, for example LED Drive Amplifiers, Relay Drive Amplifiers, Audio Amplifiers.
Data: Voltage between Collector and Emitter 3 - 20Volts max.
- Power handling capacity 100 mWatts max.
- bCurrent handling capacity 300 mAmps max.
- Amplification (gain) greater than 125.