Gauges: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m (Added links) |
m (Corrected links) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marking_gauge '''Marking Gauge'''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marking_gauge '''Marking Gauge'''] | ||
| Used to scribe lines parallel to the | | Used to scribe lines parallel to the '''[[Face Side and Face Edge|Face Edge]]''' or '''[[Face Side and Face Edge|Face Side]]''' of timber or similar materials ''(i.e. used in much the same way that '''[[Oddleg Calipers|Oddlegs]]''' are used by metalworkers)''. | ||
| [[File:MarkingGauge3.png|200px|right]] | | [[File:MarkingGauge3.png|200px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 13:16, 22 July 2015
Gauges are mainly used in designing and making to measure, mark or transfer distances.
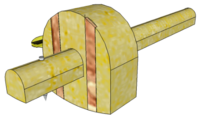
| Marking Gauge | Used to scribe lines parallel to the Face Edge or Face Side of timber or similar materials (i.e. used in much the same way that Oddlegs are used by metalworkers). | |
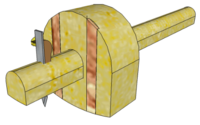
| Cutting Gauge | The small cutting blade is used instead of the normal spur of a Marking Gauge when lines have to be scribed across the grain (e.g. when marking out a shoulder for a Housing Joint) | |
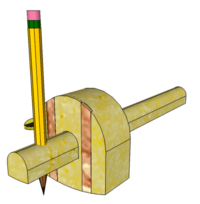
| Pencil Gauge | Sometimes scribing a line into the surface would be detrimental to the finished product and so, although less accurate, a pencil can be used instead of either a spur or a blade (e.g. when marking a bevel or chamfer) | |
| Mortise Gauge (aka Mortice Gauge) | These are similar to a Marking Gauge but have two spurs which are set a distance apart equal to the Mortise Chisel to be used when marking out for a Mortise and Tenon Joint for example. | |
| Bevel Gauge (aka Bevel Square or Sliding Bevel) | These are used to copy or mark angles other than the more common 90 degrees or 45 degrees. |