Jigs and Fixtures: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
m Added Products |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| Cutting neat circles with a '''[[Router]]''' is most easily accomplished with a '''[[Jig]]'''. Most of these, in essence, transform the '''[[Router]]''' into a '''[[Dividers and Compasses|Beam Compass]]''' by attaching it to bars or a plate rotating round a fixed point at a centre | | Cutting neat circles with a '''[[Router]]''' is most easily accomplished with a '''[[Jig]]'''. Most of these, in essence, transform the '''[[Router]]''' into a '''[[Dividers and Compasses|Beam Compass]]''' by attaching it to bars or a plate rotating round a fixed point at a centre | ||
| [[File:81heqjW8iXL. SL1500 .png|200px|right]] | | [[File:81heqjW8iXL. SL1500 .png|200px|right]] | ||
|- | |||
| '''<dtamazon type="search">PCB Holder Jig</dtamazon>''' | |||
| It is useful to have an 'extra pair of hands' when '''[[Soft Soldering]]''' components into place on a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) for example. Various clamps, special purpose vices and holders are available for this purpose. | |||
| [[File:PCBHolderJig.png|200px|right]] | |||
|- | |||
| '''<dtamazon type="search">Honing Guide</dtamazon>''' | |||
| Sharp edge tools such as plane irons or wood chisels are usually [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grinding_%28abrasive_cutting%29 ground] to an angle of 20° to 25° using a '''[[Tool Grinder]]''' then [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Honing_%28metalworking%29 ‘honed’] at an angle of 25° to 30° ''(i.e. 5° greater than the grinding angle)'' on a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sharpening_stone sharpening stone] such as an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sharpening_stone#Whetstones_and_oilstones '''Oilstone''']. Clamps and guides are available to hold the blade at the correct angle whilst using the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sharpening_stone#Whetstones_and_oilstones '''Oilstone'''] | |||
| [[File:HoningGuide.png|200px|right]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:37, 27 December 2017
Jigs and Fixtures
Description
Jigs are taken to be specially made, often self-made, pieces of equipment often used to guide another tool or simplify an operation. This might include Marking Out operations and so there is some overlap with Template.
Fixtures are similar but tend to be associated with devices for holding work whilst a machining operation is carried out.
Types and Applications
| Dowelling Jig |
Various devices have been developed to simplifying the making of Dowel Joints. A Dowelling Jig |
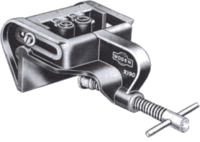 |
| Pocket Screw Jig |
Screw Pockets are holes drilled at an angle to the work surface to Counterbore the screw head. They can be used where it is not possible to screw directly through one part of the joint to the other (e.g. need to conceal screw heads or lack of access). Various Drilling Jigs are commercially available to ease the drilling of the holes to the required shallow angle (usually 15°). |  |
| Router Jig for Cutting Circles |
Cutting neat circles with a Router is most easily accomplished with a Jig. Most of these, in essence, transform the Router into a Beam Compass by attaching it to bars or a plate rotating round a fixed point at a centre | 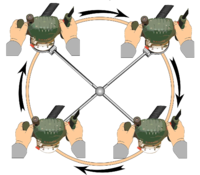 |
| PCB Holder Jig |
It is useful to have an 'extra pair of hands' when Soft Soldering components into place on a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) for example. Various clamps, special purpose vices and holders are available for this purpose. | 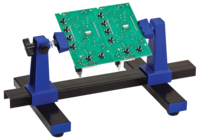 |
| Honing Guide |
Sharp edge tools such as plane irons or wood chisels are usually ground to an angle of 20° to 25° using a Tool Grinder then ‘honed’ at an angle of 25° to 30° (i.e. 5° greater than the grinding angle) on a sharpening stone such as an Oilstone. Clamps and guides are available to hold the blade at the correct angle whilst using the Oilstone | 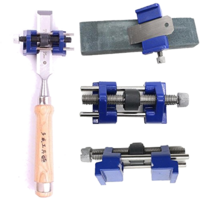 |