Relays: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m Added Template |
m Added category links |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:Secondary]] | |||
[[Category:Components]] | |||
[[Category:Electronics and Control]] | |||
Revision as of 15:10, 28 April 2015
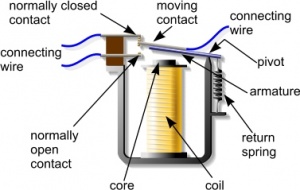
A relay is a device which uses a small control current to switch a much larger load current.They are used in switching circuits where the output of that circuit has insufficient power to drive the output device.
They have disadvantages in that they can only operate at low switching speeds and are relatively expensive.
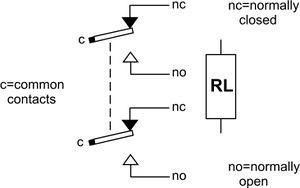
The symbol for a double pole, single throw (DPST) relay is shown together with a more simple representation of a relay for use in circuit diagrams.
Relays, in common with many other electronic devices which include movement and an electro-magnetic coil, usually have a diode connected in parallel to them to prevent damage caused by Back-EMF

A Reed Relay is a reed switch enclosed in a solenoid.

A Solid State Relay (SSR) is a solid state electronic component that provides a similar function to an electromechanical relay but does not have any moving components, increasing long-term reliability.