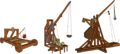The Romans: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[File:Roman siege machines.gif|500px|right|Roman siege machines]] | [[File:Roman siege machines.gif|500px|right|Roman siege machines]] | ||
A topic on Romans could involve work on a variety of short focussed tasks or design make activities. Most are likely to involve models and might include: | A topic on Romans could involve work on a variety of short focussed tasks or design make activities. Most are likely to involve models and might include: | ||
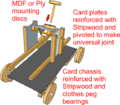
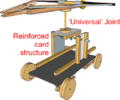
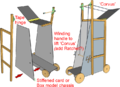
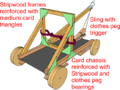
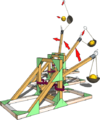
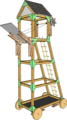
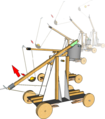
* Model Siege Weapons; | * '''[[Siege Tower|Model Siege Weapons]]'''; | ||
* Model Villas; | * Model Villas; | ||
* Jewellery; | * Jewellery; | ||
* Models of Aqueducts, Viaducts, Roads; | * '''[[Arch Bridges|Models of Aqueducts, Viaducts, Roads]]'''; | ||
* Clay Tiles for Mosaics; | * Clay Tiles for Mosaics; | ||
* ‘Finger Food’ for a Roman Feast; | * ‘Finger Food’ for a Roman Feast; | ||
* Model Trireme. | * '''[[Trireme Model|Model Trireme]]'''. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 14:11, 6 March 2018

The dominance of Ancient Greece in the Mediterranean ended when the Greeks were defeated by Rome at the Battle of Corinth (146 BC) and with emergence of the Roman Empire following the Battle of Actium in 31 BC.
In 43AD and 100 years after two previous occupations, The Romans mounted a major invasion of Britain. The Roman army was extremely well organised and equipped. They were able to overcome Celtic resistance, including a rebellion organised by Boudicca, and over the course of the next 30 years gained control of all England and Wales south of Hadrian's Wall. Some Celts made peace with the Romans, in return for keeping their lands and agreed to obey Rome, but they never conquered Scotland.
The Romans' organisational skills were used also to help administer their Empire, of which Britain was now a part. Many laws and regulations, and the idea of taking a population census, were introduced in Roman times and are still in use today. It was The Romans who added the months of July (named after Julius Ceasar), and August (named after Augustus Ceasar) to create the forerunner of the modern 12 month calendar.
They worshipped various Gods and Goddesses (i.e. Cupid, Diana, Janus, Juno, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, Minerva, Neptune, Pluto, Venus, Vesta and Vulcan). To appease their Gods, Romans would make offerings of food, flowers or money at Temples and Priests would sometimes make animal sacrifices. In 312AD, Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire.
During their occupation, they continued to be subjected to attacks from tribes north of Hadrian's Wall. Roman Britain was also under regular attack from Angles and Saxons who came across the North Sea from Germany, Denmark and the Netherlands. After some 400 years of occupation, The Romans left Britain in AD410 because they were recalled to Rome to defend their own homes against attacking Barbarians. The people of Britain were told that they no longer had a connection to Rome and that they should defend themselves against the invading Saxons.
The Romans completed many great civic works including roads, bridges, aqueducts, public baths and villas for the more wealthy. To achieve some of this, they invented and used a form of Concrete. Larger villas had a form of under-floor Central Heating and some buildings were decorated with colourful Mosaics on the walls and floors. Trade and industry flourished under Roman rule.

A topic on Romans could involve work on a variety of short focussed tasks or design make activities. Most are likely to involve models and might include:
- Model Siege Weapons;
- Model Villas;
- Jewellery;
- Models of Aqueducts, Viaducts, Roads;
- Clay Tiles for Mosaics;
- ‘Finger Food’ for a Roman Feast;
- Model Trireme.
Pages in category "The Romans"
The following 16 pages are in this category, out of 16 total.
Media in category "The Romans"
The following 39 files are in this category, out of 39 total.
-
A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities.JPG 216 × 354; 23 KB
-
BallistaChargedLabelled.png 746 × 314; 149 KB
-
Ballistae.png 1,298 × 437; 357 KB
-
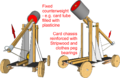
BallistaeChassisLabelled.png 574 × 501; 159 KB
-
BallistaeLabelled.png 758 × 228; 142 KB
-
BallistaTensionJavelinAssyLabelled.png 520 × 433; 135 KB
-
BallistaTensionJavelinLabelled.png 512 × 381; 178 KB
-
BallistaTorsionJavelinLabelled.png 505 × 430; 153 KB
-
BasicFrame.png 731 × 396; 101 KB
-
BoxModelRams.png 1,351 × 526; 517 KB
-
BoxModelTurris2.png 718 × 522; 139 KB
-
Gallery.png 500 × 547; 258 KB
-
MangonelBoxBaseLabelled.png 404 × 529; 92 KB
-
MangonelC.jpg 3,024 × 4,032; 1.19 MB
-
MangonelCardBaseLabelled.png 489 × 434; 122 KB
-
MusculusAssy.png 1,819 × 544; 813 KB
-
MusculusRoof1.png 592 × 397; 109 KB
-
MusculusRoofAssy.png 386 × 567; 206 KB
-
MusculusTestudo2.png 585 × 290; 195 KB
-
Onager.png 561 × 407; 123 KB
-
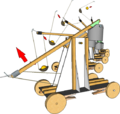
OnagerCardBaseTriggerLabelled.png 647 × 485; 207 KB
-
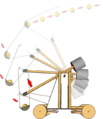
OnagerFiring.png 462 × 555; 134 KB
-
OnagerFiring2.png 842 × 503; 247 KB
-
OnagerTrebuchets.png 1,138 × 510; 359 KB
-
RomanSiege.png 552 × 237; 185 KB
-
SiegeTower.png 337 × 605; 135 KB
-
StripwoodRams.png 1,827 × 588; 866 KB
-
StripwoodTurris.png 870 × 511; 401 KB
-
TestudoConstructions.png 1,475 × 683; 809 KB
-
TorsionBallistaLabelled.png 638 × 380; 176 KB
-
TrebuchetFCW-FiringFrames.png 546 × 633; 170 KB
-
TrebuchetFCW-Labelled.png 909 × 588; 289 KB
-
TrebuchetHCW-2-Labelled2.png 892 × 621; 333 KB
-
TrebuchetHCW-Firing.png 559 × 533; 154 KB
-
TrebuchetHCW-FiringB.png 533 × 606; 150 KB
-
Vinea.png 450 × 480; 161 KB
-
VineaAssemble.png 436 × 512; 151 KB
-
Vineae.png 396 × 282; 123 KB
-
VineaeGallery.png 1,168 × 525; 471 KB