Pneumatic Control Valves: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m Added Template |
m Added category links |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[File:5pcyl.gif|600px|center]] | [[File:5pcyl.gif|600px|center]] | ||
[[Category:Secondary]] | |||
[[Category:Pneumatics]] | |||
[[Category:Components]] | |||
Revision as of 16:02, 28 April 2015

Valves control the switching and routing of the air in a pneumatic system. From studying the operation of cylinders, you may have already worked out that valves not only have to control the flow of compressed air, they also have to control the flow of exhaust air to the atmosphere. There are two main types of valves used in pneumatic switching circuits, the 3/2 valve and the 5/2 valve.
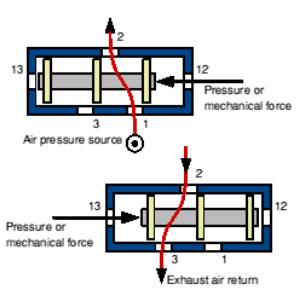
The 3/2 valve is used to control items such as single acting cylinders which have a single input. The input to the cylinder is connected to port 2, the air supply to port 1 and port 3 is allowed to exhaust to atmosphere.
The number 3 signifies that the valve has three ports, whilst the number 2 signifies that the valve has 2 directions or states.
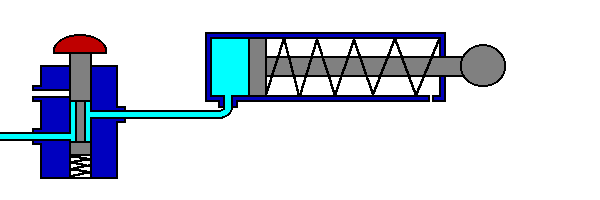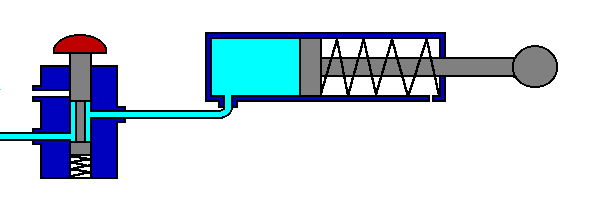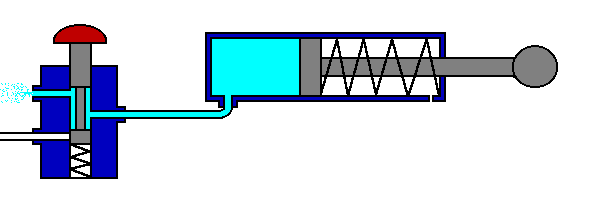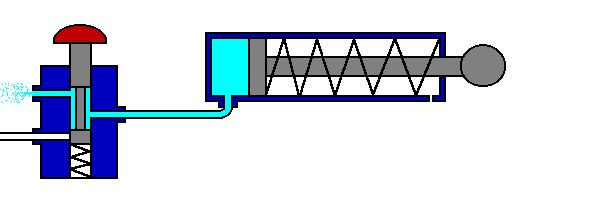
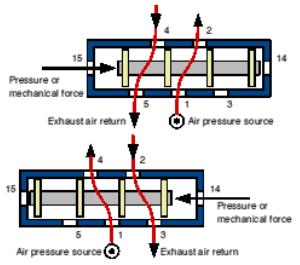
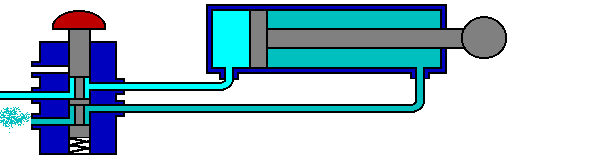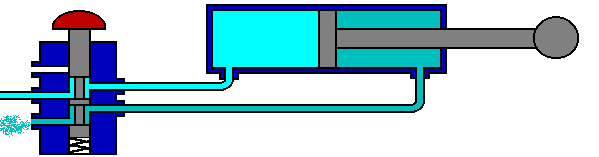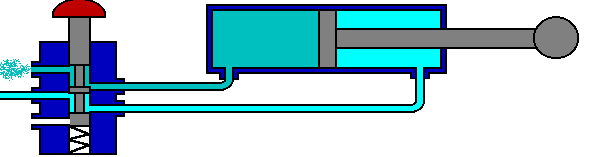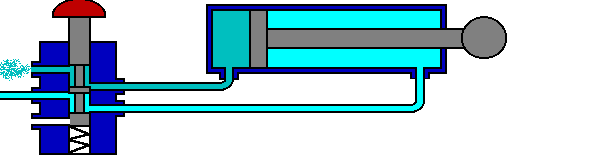
The 5/2 valve is used to control items such as double acting cylinders which have two inputs. The inputs to the cylinder are connected to ports 2 and 4, the air supply to port 1. Ports 3 and 5 are allowed to exhaust to atmosphere.
The number 5 signifies that the valve has five ports, whilst the number 2 signifies that the valve has 2 directions or states.