Transistor: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m Added category link |
m Added Template |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Transistors come in '''NPN''' and '''PNP''' types. It is important to use the correct type when designing and building circuits. | Transistors come in '''NPN''' and '''PNP''' types. It is important to use the correct type when designing and building circuits. | ||
{{Secondary Electronics}} | |||
Revision as of 12:48, 16 November 2014
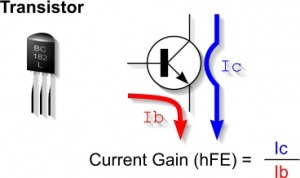
Transistors are used as electronic switches and current amplifiers. They have three ‘legs’ - base , collector and emitter. A small current to the base switches on the transistor allowing a much larger current to flow between collector and emitter.
The current gain of a transistor (hFE) is the ratio of the current flowing through the collector, to the current flowing through the base. It is a measure of the transistor's ability to amplify current (hFE = Ic/Ib).
They come in various different shapes and sizes and it is important to decide which type is required at the outset. Factors to be considered are voltage and power handling capacities, cost and availability.
Transistors require a base voltage of at least 0.6V with respect to the emitter to ‘turn on’. (Darlington Pair transistors require 1.2 V). A limiting resistor - typically 1K is required in the base circuit of the transistor stage to prevent over-running and hence overheating and destruction of the transistor.
Transistors come in NPN and PNP types. It is important to use the correct type when designing and building circuits.