Electric Bells and Buzzers: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
The purpose of the '''IN4001 [[Diode]]''' shown is to restrict any [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counter-electromotive_force '''Back EMF'''] resulting from the Transistor being used to switch an inductive device ''(e.g. '''[[Electric Motor]]''', '''[[Solenoid]]''' or '''[[Relays|Relay]]'''). | The purpose of the '''IN4001 [[Diode]]''' shown is to restrict any [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counter-electromotive_force '''Back EMF'''] resulting from the Transistor being used to switch an inductive device ''(e.g. '''[[Electric Motor]]''', '''[[Solenoid]]''' or '''[[Relays|Relay]]'''). | ||
[[File:PiezoTransducer.jpg|200px|right]] | |||
=====Piezo Transducer===== | |||
When an electric current is passed through some ceramic or crystal materials ''(e.g. quartz)'' the '''[[Crystalline Structures|Crystalline Structure]]''' expands slighty. If a piece of such a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piezoelectricity '''Piezoelectric Electric'''] material is '''[[Laminated]]''' to a thin metal plate, or diaphram, its expansion will cause the diaphram to distort slighty. When excited by an alternating current, it will vibrate the diaphram and a high frequency sound will be emitted - see '''[[Piezo Transducer]]'''. | |||
This forms the basis of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piezoelectric_speaker '''Piezoelectric Buzzers'''] or speakers which are commonly used in electronic devices and are sometimes used as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tweeter '''Tweeters'''] in less-expensive speaker systems. | |||
Revision as of 08:09, 18 August 2017
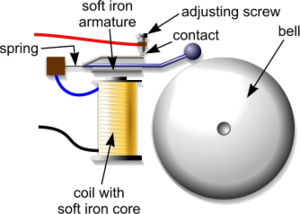
Bells
Electric bells are electromagnetic devices with contacts arranged so that once the coil is energized the armature is attracted to it and the circuit is broken.
Once broken the coil is de-energized and the armature springs back to complete the circuit once more.
Each time the armature is attracted to the coil the hammer strikes the bell. This continues in an oscillatory manner until the power is switched off.
Bells normally work on low voltage typically 6 volts. Bells are used as outputs for alarm circuits.
Buzzers

Buzzers are usually of the single tone variety and are normally rated between 6 and 24 volts.
They are suitable for alarm circuits, test equipment, timing and control.
To achieve maximum sound output from the device it should be firmly mounted.
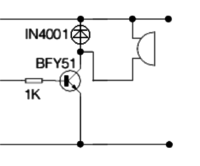
Bells and Buzzers in a Transistor Circuit
When a voltage is applied to the terminals of the bell or buzzer, they emit sounds suitable for alarm circuits and warning applications. To ensure maximum sound output, the bell or buzzer should be firmly mounted.
The purpose of the IN4001 Diode shown is to restrict any Back EMF resulting from the Transistor being used to switch an inductive device (e.g. Electric Motor, Solenoid or Relay).
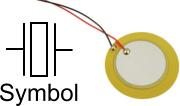
Piezo Transducer
When an electric current is passed through some ceramic or crystal materials (e.g. quartz) the Crystalline Structure expands slighty. If a piece of such a Piezoelectric Electric material is Laminated to a thin metal plate, or diaphram, its expansion will cause the diaphram to distort slighty. When excited by an alternating current, it will vibrate the diaphram and a high frequency sound will be emitted - see Piezo Transducer.
This forms the basis of the Piezoelectric Buzzers or speakers which are commonly used in electronic devices and are sometimes used as Tweeters in less-expensive speaker systems.








