Capacitor
From DT Online
Capacitors are used to store electric charge which can be released into a circuit when required. The unit of capacitance is the farad which is a very large unit, named after Michael Faraday.
Most commonly used capacitors are rated in microfarads - µF (millionths).
Large value capacitors are often used as smoothing capacitors in A.C. power supplies. Other uses for capacitors are in timing circuits and filter circuits.
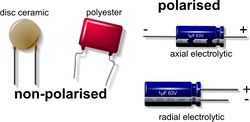
There are two main types of capacitor - polarized and non-polarized.
Capacitors can be joined together in parallel.

In this arrangement the total capacitance is equal to the value of all the capacitors added together - i.e. : C(Total)= C1 + C2 + C3...etc
Capacitors may also be connected together end to end in series.
In this arrangement the total capacitance is calculated as follows:
- ___1___ = _______1______
- C (Total) C1 + C2 + C3...etc

or
- C (Total) = _____C1xC2xC3____
- C1xC2+C2xC3+C3xC1

Capacitors may also be connected together end to end in series with a resistor to create a resistor–capacitor circuit (RC circuit) in which a capacitor charges or discharges through a resistor for a known period of time known as the time constant
In this arrangement the time constant is calculated as follows:
- T(seconds)= C(farads) x R(ohms)