Gears: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
(Created Category Gears) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:GearsAbstract.jpg|400px|right]] | ||
__TOC__ | |||
=====Description===== | |||
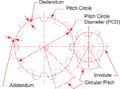
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gear '''Gears'''] ''(or 'cogs')'' are wheels whose perimeter is made up of evenly sized and spaced teeth. The teeth of one gear mesh with those of an adjoining one and transmit rotary motion between the two gears. | |||
A gear will always rotate in an opposite direction to the gear it meshes with. | |||
=====Uses===== | |||
If both gears have the same number of teeth, they will rotate at the same speed, however if they have different numbers of teeth then the gear with fewer teeth will rotate more quickly - i.e. the '''[[Velocity Ratio]]''' ''(or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gear_ratio ‘Gear Ratio’])'' of a pair of meshing gears is given as the ''Number of Teeth of the Driver Gear divided by the Number of Teeth'' of the Driven Gear. | |||
The '''[[Mechanical Advantage]]''' ''(or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Torque ‘Torque Ratio’])'' similarly is given as ''No. of Teeth on Driven divided by No. of Teeth on Driver''. | |||
---- | |||
{{Gears Buyers Guide}} | |||
=====More on Gears===== | |||
---- | |||
[[Category:Primary]] | [[Category:Primary]] | ||
[[Category:Secondary]] | [[Category:Secondary]] | ||
[[Category:Mechanisms]] | [[Category:Mechanisms]] | ||
[[Category:Materials and Components]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:14, 4 August 2016
Description
Gears (or 'cogs') are wheels whose perimeter is made up of evenly sized and spaced teeth. The teeth of one gear mesh with those of an adjoining one and transmit rotary motion between the two gears.
A gear will always rotate in an opposite direction to the gear it meshes with.
Uses
If both gears have the same number of teeth, they will rotate at the same speed, however if they have different numbers of teeth then the gear with fewer teeth will rotate more quickly - i.e. the Velocity Ratio (or ‘Gear Ratio’) of a pair of meshing gears is given as the Number of Teeth of the Driver Gear divided by the Number of Teeth of the Driven Gear.
The Mechanical Advantage (or ‘Torque Ratio’) similarly is given as No. of Teeth on Driven divided by No. of Teeth on Driver.
|
Click top left to enlarge |
More on Gears
Pages in category 'Gears'
The following 8 pages are in this category, out of 8 total.
Media in category 'Gears'
The following 9 files are in this category, out of 9 total.
- G.gif 152 × 166; 91 KB
- G2.gif 248 × 280; 131 KB
- G3.gif 248 × 280; 128 KB
- G4.gif 248 × 280; 176 KB
- GearNomenclature.png 764 × 565; 34 KB
- GearsAbstract.jpg 500 × 354; 21 KB
- Magnetic cogwheel1.gif 400 × 234; 57 KB
- Magnetic gear 26 o.gif 250 × 250; 170 KB
- R.gif 248 × 152; 79 KB