Cylindrical Cam: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
(Changed Image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:CylindricalCam. | [[File:CylindricalCam.png|200px|right]] | ||
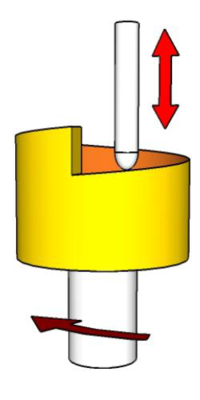
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam#Cylindrical_cam '''Cylindrical Cams'''] are used mainly to convert '''[[Types of Motion|rotational motion]]''' to '''[[Types of Motion|linear motion]]''' parallel to the rotational axis of the cylinder. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam#Cylindrical_cam '''Cylindrical Cams'''] are used mainly to convert '''[[Types of Motion|rotational motion]]''' to '''[[Types of Motion|linear motion]]''' parallel to the rotational axis of the cylinder. | ||
Revision as of 18:35, 21 February 2015
Cylindrical Cams are used mainly to convert rotational motion to linear motion parallel to the rotational axis of the cylinder.
A Swashplate may be regarded as a simple form of cylindrical cam.
Note: They can be modelled by constructing a Displacement Diagram to use as a template then cutting it out of paper and wrapping it around a tube to show the profile to be cut.
Properly machined cylindrical cams, as used in engine gearboxes for example, may have slots milled into the side of the cylinder such that the follower is positively driven each way and does not rely on a spring for its return