Router: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
(Created article) |
(Added Templates and Jigs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Some appear similar to '''[[Milling Machine|End Mills]]''' but their cutting action is different and they operate at higher cutting speeds. | Some '''Router Bits''' appear similar to '''[[Milling Machine|End Mills]]''' but their cutting action is different and they operate at higher cutting speeds. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
=====Router Templates and Guides===== | |||
[[File:RouterTemplates.png|300px|right]] | |||
'''Routers''' can be guided freely by hand but are best used if guided against a '''Fence''' or guide bar of some kind. For more complex cuts, simple '''Templates''' can be cut out of 6mm sheet MDF for example and the '''Router''' guided around the inside or outside of their shape. | |||
To prevent the revolving cutter rubbing against the '''Template''', some cutters are produced with a bearing around the top of the '''Shank''' but '''Guide Bushes''' are also available. | |||
In essence these provide a short tube ''(or bush)'' which is fixed to the underside of the '''Router''' baseplate and shrouds the top of the cutter. The size of a '''Template''' needs to be adjusted to accommodate the size of the '''Guide Bush'''. | |||
---- | |||
=====Dovetail Jig===== | |||
[[File:DovetailJig.png|300px|right]] | |||
Dovetail Jigs enable the two pieces of timber making the joint to be clamped together with a '''Template''' comprising a series of equally spaced guide slots. A '''Router''' equipped with a '''Dovetail Cutter''' is simply passed along each slot in turn to cut both halves of the eventual '''Lap Dovetail''' joint. | |||
<span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | |||
Dovetail Jigs produce '''[[Lap Dovetail|Lap Dovetails]]''' which are easily identified by their rounded edges on one side of the '''''tails''''' and the bottom of the '''''pins'''''. They are also equi-spaced, whereas through '''Dovetails''' are hand-cut and often distinguished by their wide '''''tails''''' and narrow '''''pins'''''. | |||
</span> | |||
If the '''Dovetail Cutter''' is replaced by a straight '''Router Cutter''', the same jig can be used to produce '''[[Comb Joint|Comb Joints]]''' | |||
[[Category:Portable Power Tools]] | [[Category:Portable Power Tools]] | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 30 January 2016
Portable Routers are used to produce recesses in the surface of materials (usually timber or plastics) or to finish edges of boards. Originally a hand tool, modern portable powered Routers may be regarded as the woodworker's version of a Milling Machine and CNC Routers are available.
Most models are Plunge Routers in that the cutter can be lowered into the work-piece and then locked to the required cutting depth. Router Bits can be made of High Speed Steel (HSS) but Tungsten Carbide Tipped (TCT) tools last longer and are preferred.
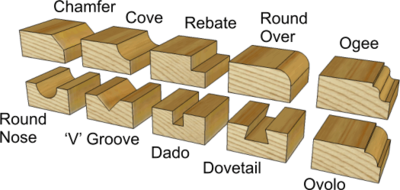
Router Bits are available in a wide variety of shapes to create different edge profiles.
Some Router Bits appear similar to End Mills but their cutting action is different and they operate at higher cutting speeds.
Safety Point! All high-speed woodcutting machinery is dangerous and Routers must only be used by trained adults or trainees under direct supervision.
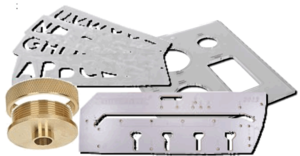
Router Templates and Guides
Routers can be guided freely by hand but are best used if guided against a Fence or guide bar of some kind. For more complex cuts, simple Templates can be cut out of 6mm sheet MDF for example and the Router guided around the inside or outside of their shape.
To prevent the revolving cutter rubbing against the Template, some cutters are produced with a bearing around the top of the Shank but Guide Bushes are also available.
In essence these provide a short tube (or bush) which is fixed to the underside of the Router baseplate and shrouds the top of the cutter. The size of a Template needs to be adjusted to accommodate the size of the Guide Bush.
Dovetail Jig
Dovetail Jigs enable the two pieces of timber making the joint to be clamped together with a Template comprising a series of equally spaced guide slots. A Router equipped with a Dovetail Cutter is simply passed along each slot in turn to cut both halves of the eventual Lap Dovetail joint.
Note:
Dovetail Jigs produce Lap Dovetails which are easily identified by their rounded edges on one side of the tails and the bottom of the pins. They are also equi-spaced, whereas through Dovetails are hand-cut and often distinguished by their wide tails and narrow pins.
If the Dovetail Cutter is replaced by a straight Router Cutter, the same jig can be used to produce Comb Joints