Types of Motion
From DT Online
| Linear Motion |
|
|
| Rotational Motion |
|
|
| Reciprocating Motion |
|
|
| Oscillating Motion |
|
Linear and Rotational Motions may maintain a constant speed, or velocity, or may accelerate and slow down (i.e. decelerate or retard). Both Reciprocating and Oscillating Motions however, by their nature, must accelerate and decelerate during each cycle of operation (i.e. as the movement reverses). The pattern of acceleration (or deceleration) may exhibit different characteristics according to design requirements as follows:
| Constant Velocity (CV) |
|
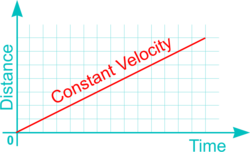 |
| Uniform Acceleration and Retardation (UAR) |
|
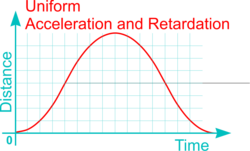 |
| Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) |
|
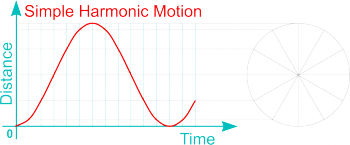 |



