Keys, Keyways and Splines: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
Created Article |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Keyseating.jpg|right|275px|Keyseating|link=https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keyseating.jpg]] | |||
__TOC__ | |||
=====Description===== | |||
Components including '''[[:Category:Gears|Gears]]''', '''[[:Category:Pulleys|Pulleys]]''' or '''[[:Category:Cams|Cams]]''' often need to be fixed to a drive shaft or axle such that they rotate with the shaft. | Components including '''[[:Category:Gears|Gears]]''', '''[[:Category:Pulleys|Pulleys]]''' or '''[[:Category:Cams|Cams]]''' often need to be fixed to a drive shaft or axle such that they rotate with the shaft. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 10: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | <span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | ||
When making simple working models in wood, drilling a tight size hole or even gluing is usually sufficient | When making simple working models in wood, drilling a tight size hole, or even gluing, is usually sufficient | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 14: | Line 20: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
In some circumstances, the component has to not only rotate with the shaft but also slide along it as it rotates ''(e.g. in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_%28mechanics%29 '''Gear Boxes'''])''. In these situations a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spline_%28mechanical%29 '''Spline Shaft'''] could be used. | In some circumstances, the component has to not only rotate with the shaft but also slide along it as it rotates ''(e.g. in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_%28mechanics%29 '''Gear Boxes'''])''. In these situations a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spline_%28mechanical%29 '''Spline Shaft'''] could be used. | ||
=====Features and Applications===== | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_screw '''Use of Grub Screws on a Plain Shaft'''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set_screw '''Use of Grub Screws on a Plain Shaft'''] | ||
| This is a relatively straightforward means of attaching components to shafts suitable for light to moderate loading. It requires no special tooling needing only holes to be drilled and tapped into the body of the component. | | This is a relatively straightforward means of attaching components to shafts suitable for light to moderate loading. It requires no special tooling needing only holes to be drilled and tapped into the body of the component. <span style="color: green">''('''Note:''' the two Grub Screws are positioned at 90° to each other such that the shaft is pressed against the inside surface of the bore rather than being held only between the two screw ends, as would be the case if they were opposite each other).''</span> | ||
| [[File:ScrewedCollarPlainShaft.png|150px|right]] | | [[File:ScrewedCollarPlainShaft.png|150px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 29: | Line 38: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Key_%28engineering%29#Parallel_keys '''Feather Key''' ''(aka Flat Key)''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Key_%28engineering%29#Parallel_keys '''Feather Key''' ''(aka Flat Key)''] | ||
| | | These can be used at any point along the shaft to provide a very positive location and capable of transmitting high loads ''(may need spacers or the presence of other components to prevent movement along the axis of the shaft)''. The '''Keyway''' can be cut using a '''[[Milling Machine|End Mill]]'''. | ||
| [[File:FeatherKeyAssy.png|200px|right]] | | [[File:FeatherKeyAssy.png|200px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 37: | Line 46: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Key_%28engineering%29#Tapered_keys '''Gib Head Key'''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Key_%28engineering%29#Tapered_keys '''Gib Head Key'''] | ||
| Useful when | | Useful when the components fitted at the end of a shaft may need to be removed easily - the key is removed by striking a wedge-shaped '''[[:Category:Punches|drift]]''' between the head and the component. The '''Keyway''' can be cut using a '''[[Milling Machine]]''' with a '''Side and Face Cutter''' or a '''Slitting Saw'''. | ||
| [[File:GibHeadKeyAssy.png|200px|right]] | | [[File:GibHeadKeyAssy.png|200px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 46: | Line 55: | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spline_%28mechanical%29 '''Splined Shaft'''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spline_%28mechanical%29 '''Splined Shaft'''] | ||
| In common use in car gearboxes and also the main transmission shaft which has to be telescopic to allow for the movement of car supension. | | In common use in car gearboxes and also the main transmission shaft which has to be telescopic to allow for the movement of car supension. | ||
| [[File: | | [[File:Splines.png|200px|right]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Keyways Buyers Guide}} | |||
[[Category:Fixings and Fastenings]] | [[Category:Fixings and Fastenings]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:30, 6 June 2018

Description
Components including Gears, Pulleys or Cams often need to be fixed to a drive shaft or axle such that they rotate with the shaft.
This can be achieved by making the hole a very tight fit on the shaft (known to Engineers and Mechanics as a Press Fit or Interference Fit) but this is not suitable if the component has to be removable.
Note: When making simple working models in wood, drilling a tight size hole, or even gluing, is usually sufficient
Grub Screws can be used where the loading is not high but otherwise Keys are preferred.
Note: When using Grub Screws a better grip can be achieved if two are used but these must be positioned at 90° to each other. Alternatively, the screw can be tightened on to a 'flat' which has been filed or milled on to the shaft.
In some circumstances, the component has to not only rotate with the shaft but also slide along it as it rotates (e.g. in Gear Boxes). In these situations a Spline Shaft could be used.
Features and Applications
| Use of Grub Screws on a Plain Shaft | This is a relatively straightforward means of attaching components to shafts suitable for light to moderate loading. It requires no special tooling needing only holes to be drilled and tapped into the body of the component. (Note: the two Grub Screws are positioned at 90° to each other such that the shaft is pressed against the inside surface of the bore rather than being held only between the two screw ends, as would be the case if they were opposite each other). | 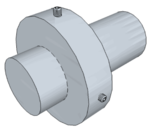 |
| Grub Screw mated on to a ‘Flat’ | Screws located on to a ‘flat’ can increase the resistance to slippage and help align components along a shaft. | 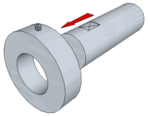 |
| Use of a Squared Shaft | Suitable only where a component is fitted at the end of a shaft but capable of transmitting very high loads and provides a positive location of the component in one of four positions. | 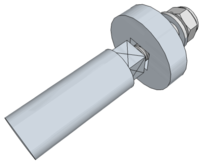 |
| Feather Key (aka Flat Key) | These can be used at any point along the shaft to provide a very positive location and capable of transmitting high loads (may need spacers or the presence of other components to prevent movement along the axis of the shaft). The Keyway can be cut using a End Mill. | 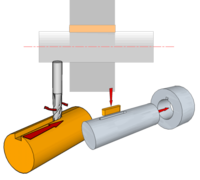 |
| Woodruff Key | In common use on tapered shafts because they can tilt to accommodate the taper angle. The Keyway is cut using a Woodruff Cutter in a Milling Machine. | 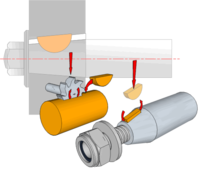 |
| Gib Head Key | Useful when the components fitted at the end of a shaft may need to be removed easily - the key is removed by striking a wedge-shaped drift between the head and the component. The Keyway can be cut using a Milling Machine with a Side and Face Cutter or a Slitting Saw. | 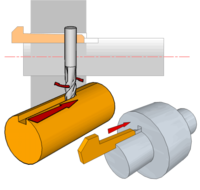 |
| Use of Drilled Holes and Pegs | A relatively simple way of providing a key-type location is to drill axially down the joint between component and shaft then inserting small rods as shown. |  |
| Splined Shaft | In common use in car gearboxes and also the main transmission shaft which has to be telescopic to allow for the movement of car supension. |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Woodruff Key Assortment |
Woodruff Key Cutter Set |
Feather Key Assortment |
End Mill Cutter Set |
Grub Screw Assortment |
Stainless Steel Full Hex Nuts. Assorted sizes |