Industrial Plastics Moulding: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m (Corrected Links) |
m (Changed main image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Www.GIFCreator.me scf30H.gif|Plastic Injection Moulding Injection Phase|400px|right|link=https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plastic_Injection_Moulding_Injection_Phase.gif]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
Revision as of 19:16, 14 November 2016
Description
Although there are ways of modelling almost all methods of moulding plastics in schools (e.g. Injection Moulding and small Injection Moulders for example are available), most working with plastics in Design and Technology involves Thermoforming (i.e. forming of heated flat sheets of plastics).
The processes listed below generally involve much more expensive plant than is normally only available in industry.
Injection Moulding
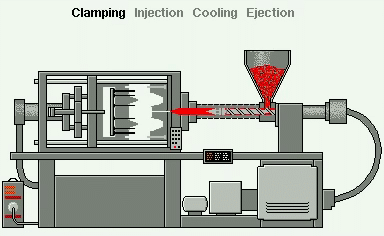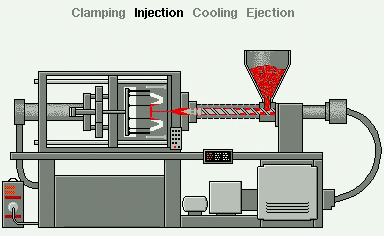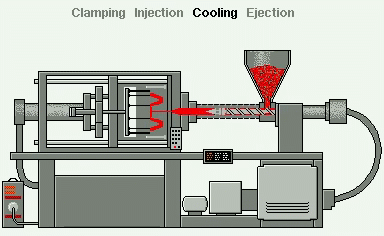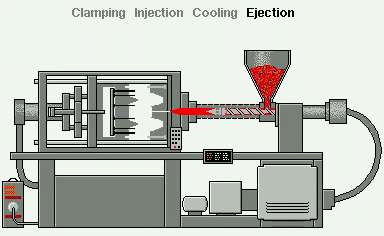
Injection Moulding is the most commonly used manufacturing process for the production of a great variety plastic products and components.
In industry, plastics granules are drawn into an Injection Moulder cylinder, or barrel, via a rotating screw to a point where they are heated and melted. The screw then operates as a piston and forces the melted plastic into a mould to create the products as shown:
- Reciprocating screw;
- Hopper;
- Granules;
- Barrel;
- Heaters;
- Mould.
As a consequence, most injection moulded products can be identified by the presence of a small ‘pip’ or sprue where the melted plastics entered the mould.
Extrusion
Extrusion.is an industrial process, usually continuous, which can be likened to squeezing toothpaste out of a tube. Small beads of a Thermoplastics are fed into a hopper from which they feed into the barrel of the Extruder.
The heated Extruder contains a rotating screw which forces the softening plastics through a Die at the end which produces the extruded profile.
The general process of Extrusion can also be used to produce aluminium sections for example, and can be a hot or cold process.for metals such as Aluminium
Calendering
Calendering is used to manufacture thin film or sheet in either plastics or paper - or both by laminating films together. The process takes heated and softened plastics and squeezes it through rollers until the required thickness is achieved. It has some superficlal similarities with that used in Steel Rolling Mills and was developed originally for the production of rubber sheet.
Calendars exert immense pressure on the material which results in lower temperatures being needed. This make the process very suitable for materials which may be sensitive to heat damage and for materials such as PVC for which there is some concern regarding fume emissions.
The last set of rollers determines the final thickness of sheet and can also impart a textured surface finish if required.
Rotational Moulding
Rotational Moulding is an industrial process in which a hollow mould is loaded with a measured amount of .Thermoplastics then heated and rotated about two axes such that the plastics forms a coating around the inside of the mould.
Rotation continues throughout both the heating and cooling phases to avoid deformation of the finished product. This makes for a long cycle times but it is still a cost-effective and easy way to produce large hollow pieces such as storage tanks.
The moulds for
Rotational Moulding are either fabricated from welded sheet steel or cast and are significantly cheaper than some other types of mould.
Compression Moulding
Compression Moulding is used to create products by placing a measured amount of Thermoset Resin into a heated mould cavity then applying the top of the mould, or plug, with heat and pressure until the resin is cured.
Compression Moulding is a high volume process at a lower cost than Injection Moulding but not as consistent, and it is difficult to control flashing. It is useful also however for moulding composite products such as when Fibreglass (GRP) reinforcement is needed.