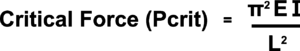Buckling: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
Created article |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:ElephantPillar2.png|200px|right]] | [[File:ElephantPillar2.png|200px|right]] | ||
A '''[[Structural Member]]''' in '''[[Compression]]''' ''(i.e. a '''[[Strut]]''')'' is more likely to [ | __TOC__ | ||
=====Description===== | |||
A '''[[Structural Member]]''' in '''[[Compression]]''' ''(i.e. a '''[[Strut]]''')'' is more likely to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buckling '''buckle'''] first when subjected to pressure - assuming the '''[[Strut]]''' is made of a sensible material and not something so [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brittleness '''brittle'''] it is likely to explode under pressure(!) | |||
::::::::::[[File:EulersBucklingEquation.png|300px|bottom]] | ::::::::::[[File:EulersBucklingEquation.png|300px|bottom]] | ||
The point at which a '''[[Strut|strut]]''' might [ | See - '''<dtamazon product="0140135979" type="text">'The New Science of Strong Materials: Or Why You Don't Fall Through the Floor' by J.E.Gordon</dtamazon>''' | ||
=====Features and Applications===== | |||
The point at which a '''[[Strut|strut]]''' might [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buckling '''buckle'''] can be assessed using a simplified form of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler's_critical_load '''Euler's Buckling Equation'''] as follows: | |||
| Line 12: | Line 22: | ||
*'''E''' = the '''[[Young's Modulus]]''' of the material ''(obtainable from tables or by experiment)''. | *'''E''' = the '''[[Young's Modulus]]''' of the material ''(obtainable from tables or by experiment)''. | ||
*'''Capital I''' = the '''[[Moment of Inertia]]''' about the '''[[Neutral Axis]]''' ''(for a rectangular beam this is its breadth times the depth cubed divided by 12)''. | *'''Capital I''' = the '''[[Moment of Inertia]]''' about the '''[[Neutral Axis]]''' ''(for a rectangular beam this is its breadth times the depth cubed divided by 12)''. | ||
*'''L''' = the length of the '''[[Strut]]''' ''(this is taken as the total length if the strut is assumed to be pin-jointed at each end but would vary with other fixing methods - see [ | *'''L''' = the length of the '''[[Strut]]''' ''(this is taken as the total length if the strut is assumed to be pin-jointed at each end but would vary with other fixing methods - see [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler's_critical_load '''Euler's Buckling Equation'''])'' | ||
{{Construction Kits Buyers Guide}} | |||
[[Category:Terminology]] | [[Category:Terminology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:27, 4 July 2017

Description
A Structural Member in Compression (i.e. a Strut) is more likely to buckle first when subjected to pressure - assuming the Strut is made of a sensible material and not something so brittle it is likely to explode under pressure(!)
See - 'The New Science of Strong Materials: Or Why You Don't Fall Through the Floor' by J.E.Gordon
Features and Applications
The point at which a strut might buckle can be assessed using a simplified form of Euler's Buckling Equation as follows:
Where:
- Pcrit = the Critical Force at which the strut will start to buckle.
- E = the Young's Modulus of the material (obtainable from tables or by experiment).
- Capital I = the Moment of Inertia about the Neutral Axis (for a rectangular beam this is its breadth times the depth cubed divided by 12).
- L = the length of the Strut (this is taken as the total length if the strut is assumed to be pin-jointed at each end but would vary with other fixing methods - see Euler's Buckling Equation)
|
Click top left to enlarge |