Ohm's Law: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
m Added category link |
m Added category links |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Category:Secondary]] | |||
[[Category:Electronics and Control]] | [[Category:Electronics and Control]] | ||
[[Category:Terminology]] | |||
Revision as of 06:56, 30 April 2015
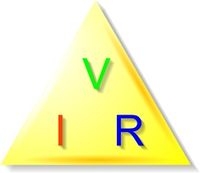
Ohm's law is an extremely useful equation in the field of electrical/electronic engineering because it describes how voltage, current and resistance are interrelated.
If the three symbols for voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R) are arranged in a triangle as shown, then the various representations of Ohm's Law can easily be seen - i.e.
- Voltage = Current x Resistance (V = I x R)
- Current = Voltage / Resistance (I = V / R)
- Resistance = Voltage / Current (R = V / I)
A similar triangular graphic may be used to show the various relationships between electrical power (watts), electrical current (amps) and voltage (volts).
Note: Abbreviations are usually named after the thing you're measuring, not the unit. So resistance is R, not O for ohms (Ω) but voltage is measured in volts, so it's V either way (the term ‘electromotive force’ and the symbol E are becoming less common, replaced by voltage and V)