Stress: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
Created article |
m Added text and image |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In engineering, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stress_%28mechanics%29 '''Stress'''] is a measure of the load applied for each unit of cross-sectional area of the material under load - i.e. '''Stress = Load / Area''' and is measured in '''[[Newton|newtons]]''' per square metre ''('''Nm<sup>-2</sup>''')'' | [[File:AtomSpringModel.png|300px|right]] | ||
In engineering, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stress_%28mechanics%29 '''Stress'''] is a measure of the load applied for each unit of cross-sectional area of the material under load - i.e. '''Stress = Load / Area''' and is measured in '''[[Newton|newtons]]''' per square metre ''('''Nm<sup>-2</sup>''')''. | |||
When a material is subjected to '''stress''' it will deform in some way ''(e.g. be stretched or squashed)'' - although for many materials this may be only by a microscopically small amount. The resulting deformation is known as '''[[Strain]]''' and dividing '''Stress''' by '''[[Strain]]''' provides a measure of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elastic_modulus '''stiffness'''] of the material known as its '''[[Young's Modulus]]''' | |||
Revision as of 13:50, 24 December 2015
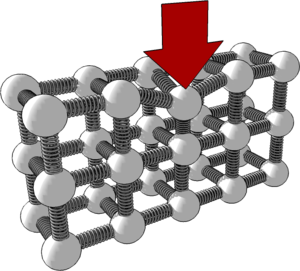
In engineering, Stress is a measure of the load applied for each unit of cross-sectional area of the material under load - i.e. Stress = Load / Area and is measured in newtons per square metre (Nm-2).
When a material is subjected to stress it will deform in some way (e.g. be stretched or squashed) - although for many materials this may be only by a microscopically small amount. The resulting deformation is known as Strain and dividing Stress by Strain provides a measure of the stiffness of the material known as its Young's Modulus
Many terms in engineering, science and mathematics are represented by Greek symbols and Stress is allocated the symbol σ (sigma).