Rivets: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Pan Head Rivet''' | | '''Pan Head Rivet''' | ||
| Used in a similar way to ''Snap Head Rivets''' but chosen where maximum strength is needed. | | Used in a similar way to '''Snap Head Rivets''' but chosen where maximum strength is needed. | ||
| [[File:PanHd.png|125px|right]] | | [[File:PanHd.png|125px|right]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 17 June 2017
Description
Rivets (aka Rivits) have various designs of head at one end and are used to fasten materials together by being passed through a punched or drilled hole and hammered over (usually) to form a head on the reverse side. They are available in several materials and sizes, can be solid or hollow and specialised designs also exist (e.g. ‘Pop’ Rivets).
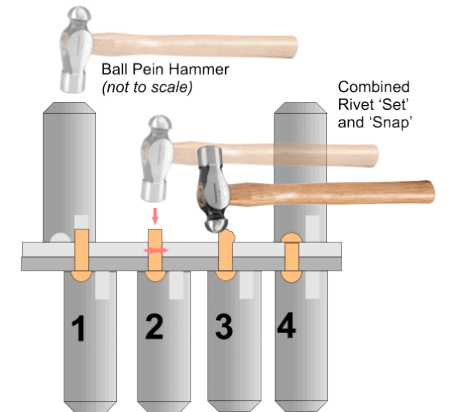
In general, Rivets are first passed through the punched or drilled holes then, with head supported on a hard surface (e.g. a Rivet Snap in the illustration shown), then a hollow tool with a hole equal to the Rivet diameter is struck down over it to squeeze, or Set, the pieces of material together (1). The tool, or Rivet Set, is removed and using a hammer, the Rivet is first struck square on to thicken it inside the holes (2), then the head is formed by hammering over (3) (and may be formed finally using the Rivet Snap (4) for these types of rivet).
Note: Where several Rivets are to be used to form a joint, it is important to drill through both parts just once initially, and this hole riveted before drilling through and riveting any further holes. This is because it is most unlikely that drilling separately would position the holes accurately enough.
Solid Rivets
| Snap Head Rivet | These round-headed rivets were commonly used in large structural work where strength is needed. In traditional boiler-making, ship building and bridge girder construction for example, large iron Snap Rivets were passed through the plates to be joined and hammered over whilst red hot. This not only made the hammering over easier but, as the iron rivet cooled, the joint tightened due to its contraction. Much of this type of work is now Welded rather than riveted. |  |
| Countersunk Head Rivet | Abbreviated to Csk.Hd Rivets, these are seated within a countersunk hole and used where a flush finish is required but, as a consequence, they support lower loads. |  |
| Flat Head Rivet | These are a compromise in that they are useful where a large protrusion might be an issue and can carry higher loads than Csk.Hd. Rivets. They useful for sheet metalwork structures where the thickness of sheet precludes countersinking. |  |
| Pan Head Rivet | Used in a similar way to Snap Head Rivets but chosen where maximum strength is needed. |  |
'Pop' Rivets
| Domed Head 'Pop' Rivet | Also known as Blind Rivets these have the advantage of being able to be applied from just one side of the material by squeezing them with Rivet Pliers or Tongs. |  |
| Large Flange 'Pop' Rivet | A large head variation, useful when rivetting together softer materials. They are often used with a Backing Washer on the reverse side if very soft materials are to be joined. |  |
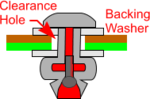
Note: Some plastics, such as Acrylic, are very Brittle and would normally shatter as the thickening 'Pop' Rivet exerts Tensile forces on the inside of the hole. To avoid this, holes for 'Pop' Rivetting plastics are drilled over-size and Backing Washers or plates of some kind are added such that the two pieces of plastics are exposed only to Compressive forces as they are squeezed together.
Specialised Rivets
| Hollow Rivet | The hollow end of these rivets means they can be closed with much less force and therefore used for lighter constructions in softer materials. |  |
| Birfurcated Rivet | Almost always used with a Backing Washer on the reverse side, these are commonly used for joining on to leather goods for example. |  |
| Rivet Nut | These provide a means of inserting a threaded hole into thin sheet materials. They are first screwed on to an adapter, on Mandrel then fixed in a similar manner to 'Pop' Rivets |  |
| Eyelet | Although not a rivet as such, these are applied in much the same way using a punch and die. They are often used to thread fixing cords or ropes to the edge of fabrics (e.g. for car trailer and boat covers) |  |











