Ancient Egyptian Survey Tools
From DT Online
Introduction
Egypt is regarded as the home of the first known Surveyors. Surveying was necessary in Ancient Egypt because the annual floods buried or destroyed boundary markers, which then had to be re-established for ownership of the fields.
Using only basic equipment the Pyramids were built and aligned with astonishing accuracy. The Great Pyramid at Giza (Khufu) has been measured at 231 meters square and the largest discrepancy is 30cm between the north and west sides - but the difference between the north and east sides is only 6cm!

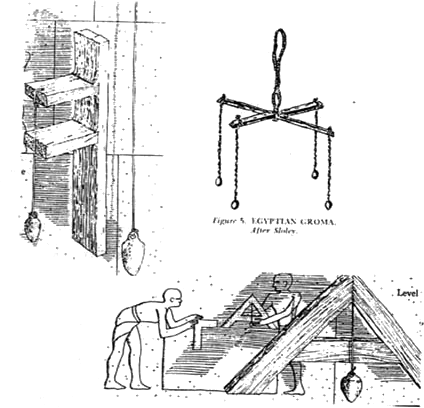
Plummet
At its simplest, a Plummet (aka Plumb Bob) is a small weight suspended on a cord and is still much in use today.
A more elaborate type of plumb was found in the tomb of the architect Senedjem at Deir el-Medina. The board was held vertically against the wall to be tested, and the plumb bob was attached to a wooden crossboard so that the cord, if in a vertical position, would touch a second cross board below, which was the same size as the first.
Once a vertical is established then horizontals can also be set by placing a Builders' Square against it. Plumb Bobs were used also to establish a vertical Datum Reference in other surveying instruments.
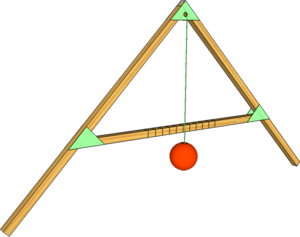
Square Level
The Square Level was the main levelling instrument used not only in Ancient Egypt but also in later Roman and medieval building although water-filled trenches may have been used to level larger distances. Smaller versions of Water Levels were developed much later. They were known to the Romans but was used by them for only special purposes.
Ancient Egyptian versions had two legs of equal length, connected at a right angles and with a cross piece to create a tool in the shape of the letter 'A'. From the connecting corner of the two legs was suspended a Plumb Bob, which could line up with a mark in the centre of the cross piece when the two legs were stood on the horizontal surface of a building stone for example.
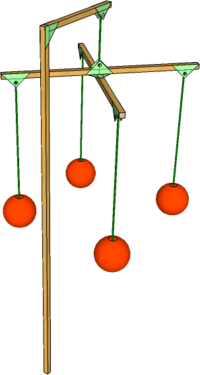
Groma
The Groma was a right-angle device designed for laying out the corners of fields, much like the Surveyors' Cross of more recent times.
The long vertical pole was set vertically in the ground at the start corner and turned until one of the cross-pieces lined up with one of the sides of the field to be set out. Sightings were then made along the second cross piece and a Ranging Pole, some distance from the Groma, aligned and set into the ground to mark a line at right angles to the first side.
Later, the Romans made great use of the Groma to set out the centee of military camps and new towns from which they then created the regular grids on which they based their town planning (i.e. cardo and decumanus grids).
Merkhet
- Structures and Frames can also be modelled using the Construction Kits listed in the Truss Bridges and Looking at Bridges articles.
Safety Point! Take great care with hot glue guns and all hot-melt glues. The melted glue can stick to the skin and cause severe burns.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Junior Hacksaw |
Clamp-on Hobby Vice |
Stripwood |
Balsa Wood |
Medium card coloured |
Thick card coloured |
Cutting Mat |
10mm Squared Paper |
PVA glue |
Glue Gun |
Bamboo Flower Sticks |
Notes:
- Choose metal cutting hacksaw blades - the teeth are small which suits this scale of work and they are safer for young children
- School PVA glue is best for young children because it is non-toxic and washes off : PVA Wood Glue is strongest but must be used with care.
- Try to get natural Flower Sticks or wear gloves because the green stain comes off on hands!