Radial Cam: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
Added Template |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:SnailCam.gif| | [[File:Cam-disc-3 3D animated.gif|100px|right]][[File:SnailCam.gif|200px|right]][[File:Lf.gif|150px|right]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
=====Description===== | =====Description===== | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam '''Radial Cams'''] are one of the most common types of ‘cam’. The ‘radial cam’ is a rotating plate or disc with an outer circumference shaped to produce a required movement ''(usually linear)'' to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam_follower '''‘follower’'''] which is held against it. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam '''Radial Cams'''] are one of the most common types of ‘cam’. The ‘radial cam’ is a rotating plate or disc with an outer circumference shaped to produce a required movement ''(usually linear)'' to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cam_follower '''‘follower’'''] which is held against it. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
=====Features and Applications===== | =====Features and Applications===== | ||
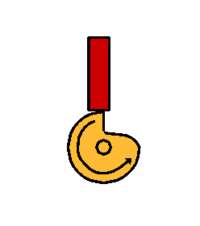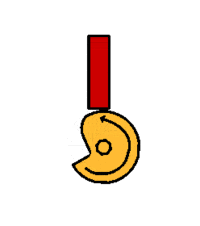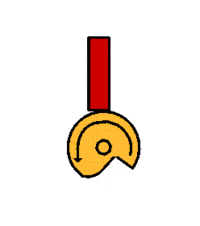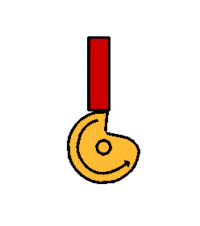
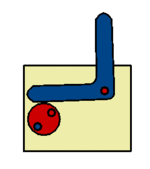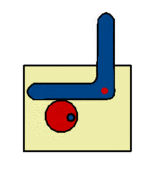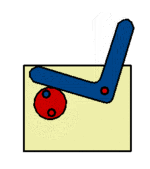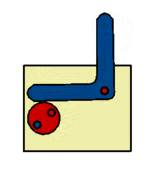
The radial cam may be a simple recognisable shape, such a circle or ellipse, or may be more a complex profile producing variations in the speed and magnitude of the follower movement, moments of ''''dwell’''' or a ''''sudden drop’''' - as with the ''' | The radial cam may be a simple recognisable shape, such a circle or ellipse, or may be more a complex profile producing variations in the speed and magnitude of the follower movement, moments of ''''dwell’''' or a ''''sudden drop’''' - as with the '''[[Snail Cam]]''' shown. The sequence of follower movements is designed using a '''[[Displacement Diagram]]''' and the cam shaped accordingly. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
Followers may also be in the form of a [[Class of Lever|lever]] and when used against these, the cam generates an '''[[Types of Motion|oscillatory movement]]'''. | Followers may also be in the form of a [[Class of Lever|lever]] and when used against these, the cam generates an '''[[Types of Motion|oscillatory movement]]'''. | ||
=====Animations===== | |||
* Examples from '''[[2100 Animated Mechanical Mechanisms|Nguyen Duc Thang's]]''' YouTube Channel '''[[2100 Animated Mechanical Mechanisms]]''' | |||
{| | |||
|- | |||
| [https://youtu.be/xGQjTeLqTq0 '''Disk Cam Operated Vice'''] - the pink cam has a rectangular slot at its centre so it has linear motion during rotation. This helps move the green clamping head longer and faster. | |||
| {{#ev:youtube|xGQjTeLqTq0|200x200|right||frame|loop=1&autoplay=0&playlist=xGQjTeLqTq0}} | |||
|} | |||
{{Cams & Cranks Buyers Guide}} | {{Cams & Cranks Buyers Guide}} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:35, 29 August 2016

Description
Radial Cams are one of the most common types of ‘cam’. The ‘radial cam’ is a rotating plate or disc with an outer circumference shaped to produce a required movement (usually linear) to a ‘follower’ which is held against it.
Features and Applications
The radial cam may be a simple recognisable shape, such a circle or ellipse, or may be more a complex profile producing variations in the speed and magnitude of the follower movement, moments of 'dwell’ or a 'sudden drop’ - as with the Snail Cam shown. The sequence of follower movements is designed using a Displacement Diagram and the cam shaped accordingly.
A 'follower’ may simply be a rod, constrained by guides, to slide up and down in a reciprocating motion, as the cam, which it rests upon, rotates underneath it - i.e. as push-rods of some car engines are driven up and down by the engine camshaft. The ends of the 'follower’ may be flat, round, wedge-shaped or pointed for different service conditions or may terminate with a roller for increased wear resistance.
Followers may also be in the form of a lever and when used against these, the cam generates an oscillatory movement.
Animations
- Examples from Nguyen Duc Thang's YouTube Channel 2100 Animated Mechanical Mechanisms
| Disk Cam Operated Vice - the pink cam has a rectangular slot at its centre so it has linear motion during rotation. This helps move the green clamping head longer and faster. |
|
Click top left to enlarge |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Engino "STEM Mechanics" Cams and Cranks Set |
Engino "STEM Mechanics" Levers and Linkages Set |
Fischertechnik 536622 - Mechanic & Static 2 |
Engino Mechanisms Set |
Engino Gears Set |