Stripwood Technology Materials: Difference between revisions
From DT Online
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battery_holder '''Battery Holders and Clips'''] | | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battery_holder '''Battery Holders and Clips'''] | ||
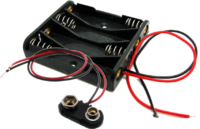
| A single battery '''''cell'''' is 1.5 volts so, in some cases, batteries need to be linked together in a '''Battery Holder''' to achieve a suitable voltage for working models ''(e.g. 4.5 or 6 volts)''. Some batteries link cells together internally to provide a higher voltage output ''(e.g PP3 batteries produce 9 volts)'' and for these, '''Battery Clips''' can be used to connect them to circuits. | | A single battery '''''cell''''' is 1.5 volts so, in some cases, batteries need to be linked together in a '''Battery Holder''' to achieve a suitable voltage for working models ''(e.g. 4.5 or 6 volts)''. Some batteries link cells together internally to provide a higher voltage output ''(e.g PP3 batteries produce 9 volts)'' and for these, '''Battery Clips''' can be used to connect them to circuits. | ||
| [[File:BatteryHolderClip.png|200px|right]] | | [[File:BatteryHolderClip.png|200px|right]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
| rowspan=2|[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copper_tape '''Copper Tape'''] | | rowspan=2|[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copper_tape '''Copper Tape'''] | ||
| rowspan=2|Self-adhesive '''Copper Tape''' provides a good way to create a circuit on paper of card - print off the circuit diagram, tape over the lines then staple components in place. | | rowspan=2|Self-adhesive '''Copper Tape''' provides a good way to create a circuit on paper of card - print off the circuit diagram, tape over the lines then staple components in place. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | <span style="color: green">'''Note:''' | ||
Revision as of 00:52, 22 March 2016
Plain, unpainted or unvarnished wood and card have a porous surface, which is easily coloured with water based paints or dyes and glued using safe, non-solvent based adhesives such as PVA.
Used cartons can be turned inside out and resealed with double-side adhesive tape or a Glue Gun such that their plain card inner surface is revealed.
"Shiny" surfaces, such as plastics, foils and metals can be glued using solvent-based or hot-melt adhesives or joined mechanically (e.g. using screws or cable ties)
Wood Based
| Stripwood | Thin strips of Softwood or Jelutong, most commonly 8mm square but also 10mm and 12mm square, provide an easy to cut and glue material for modelling (e.g. using a Junior Hacksaw and PVA). | |
| MDF or Ply Discs. | An assortment of discs, between 20mm and 80mm diameter, cut from 6mm thick MDF or Ply, each pre-drilled with a 4.5mm hole, provides the basis of most wheels and pulleys used. They can be purchased ready-made or cut from sheet using a Hole Saw.
Note: This is most easily done if the sheet is first prepared into strips slightly wider than the required diameter. |
|
| Wooden Clothes Pegs | Plain wooden spring type clothes pegs can be glued on to structures using PVA to provide a good anchorage for bearings and axles | |
| Dowel | Plain wooden dowel, 4.5mm diameter, is used for axles but 6mm, 8mm and other larger sizes can also be useful. The end of dowel can be chamfered with a pencil sharpener to make it easier to fit wheels on, for example. | |
| Matchsticks | Plain softwood matchsticks can be glued with PVA around card discs to create simple Peg and Cage Gears for example. | |
| Lolly Sticks | Plain wooden sticks can be glued with PVA for general construction detail and also larger Peg Gears | |
| Wooden Beads | Large wooden beads can, perhaps surprisingly, also be used as pulleys if using a wide elastic band. Nineteenth century factories powered their machines from a single engine driving a Line Shaft on which were arranged pulleys over each machine. The pulleys were slightly "barrel-shaped" such that the wide leather belts connecting them to the machines below, always ride to the high centre and stay on the pulleys. |
Card Based
| Card Discs | An assortment of medium card discs, between 20mm and 80mm diameter, provide flanges for pulleys and the basis for setting out any radial structure (e.g. for simple Peg Gears) | |
| Thick Card | Thick card needs to be cut with a Craft Knife and so is best presented to very young children in the form of an assortment of pre-cut rectangles from which they make a choice. For older children pre-cut strips or varying widths can be offered for them to choose from and decide on the length to cut. | |
| Card Triangles and Squares | These are cut out from medium card, Triangles can be used as Gussets to join together pieces of Stripwood by brushing on PVA glue and squares punched with a neat hole to make a Knife Edge Bearing. A useful size is 30mm x 30mm which can most easily be marked out using the width of a wooden ruler as a guide. |
Plastics Based
| PVC Tubing | Select two sizes: one which is a tight fit on dowel axles to make end caps to stop loose wheels falling off; and one which is loose fitting to make short spacers so that wheels do not rub against chassis members for example. | |
| Plastics Tubing | Rigid plastics tube (e.g. made from Acrylic) can be purchased but old Felt-Tip Pens can be disassembled and the outer casing cut to length using a Junior Hacksaw. Short pieces can be used as bearings or axle spacers.
Note: To avoid making a mess use only water based pens! |
|
| Cotton Reels | Traditional plain wooden cotton bobbins can be glued using PVA but these are hard to find. Modern plastics cotton reels need to be fixed with solvent-based adhesives or a Glue Gun. They are a loose fit on 6mm diameter dowel and useful for spacers or pulleys in addition to general construction detail. |
Components
| Cable Ties | Also known as Tie Wraps these are available in several sizes and provide a good firm fixing (e.g. for electric motors). | |
| Elastic Bands | When used as drive belts, choose narrow ones for grooved Pulleys made from card and MDF dscs. Wide elastic bands can be used as drive belts in conjunction with rounded beads. Elastic Bands provide also a quick assembly method for Bamboo Cane Structures | |
| Velcro | Self-adhesive hook and loop fastenings provide a quick and easy way to mount batteries or locate interchangeable parts of a model. | |
| Paper Clips | Unpainted Paper Clips can be used to connect battery leads to copper tape circuits or the connecting link in simple switches made with Paper Fasteners or Drawing PIns. | |
| Paper Fasteners | These can be placed through punched holes and used to make switches and contact points when building copper tape circuits on card. | |
| Drawing PIns | Also known as Thumb Tacks brass Drawing Pins can be used to make switches and contact points when building copper tape circuits on a softwood, insulation boards or corrugated plastics base. | |
| Eyelets | Brass Eyelets can provide bearings for card axle holders or join one side of a card-based copper tape circuit to the other. Eyelets can be inserted with Eyelet Pliers or use of a Eyelet Punch and Die. |
Electrics
| Battery Holders and Clips | A single battery cell is 1.5 volts so, in some cases, batteries need to be linked together in a Battery Holder to achieve a suitable voltage for working models (e.g. 4.5 or 6 volts). Some batteries link cells together internally to provide a higher voltage output (e.g PP3 batteries produce 9 volts) and for these, Battery Clips can be used to connect them to circuits. | |
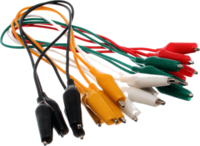
| Jumper Leads | These short test leads have a Crocodile Clip at each end making them useful for quickly connecting together electrical components to complete a circuit. | |
| Crocodile Clips | These spring loaded clips can be used to make test leads or to connect batteries to circuits. | |
| Wire | Insulated copper wire is needed to join components together. Stranded wire is the more flexible but single core wire may be easier to use in some instances. | |
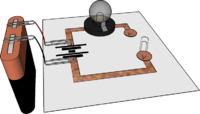
| Copper Tape | Self-adhesive Copper Tape provides a good way to create a circuit on paper of card - print off the circuit diagram, tape over the lines then staple components in place.
Note: If Copper Tape tracks cross over each other, the adhesive may prevent an electrical connection between them - which may be a good or a bad thing! Circuits can be completed using Paper Clips and Paper Fasteners or Drawing Pins to make switches and connections |
|
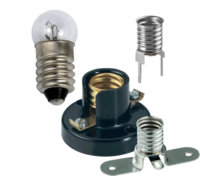
| Bulbs and Bulb Holders | Low voltage bulbs in holders provide the simplest way to see if a circuit is working and can provide lighting effects for model fairgrounds and houses for example. | |
| Model Electric Motors | Small model D.C. motors can be used to power model vehicles and fairground rides for example. Depending on their size, it may be possible to mount them using plumbers' pipe clips or Terry Clips but more usually, they can be arranged to straddle two Stripwood bearers, then fixed with a Cable Tie or glued using a Glue Gun | |
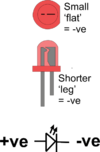
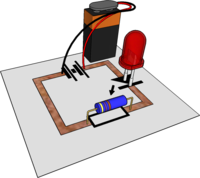
| LEDs | Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) use very little electricity and are available in a range of colours making them extremely useful for modelling. A disadvantage is that they are not as easy to use as Bulbs because:
|
|
| Resistors | Resistors can be thought of a little like a tap and they can be used to limit the amount of electricity (i.e. Current)) flowing through a circuit. Resistance is measured in Ohms and a suitable size Resistor for Stripwood Technology is 470 ohms (i.e. 470Ω). For more advanced work, Ohm's Law can be used to calculate an appropriate size |